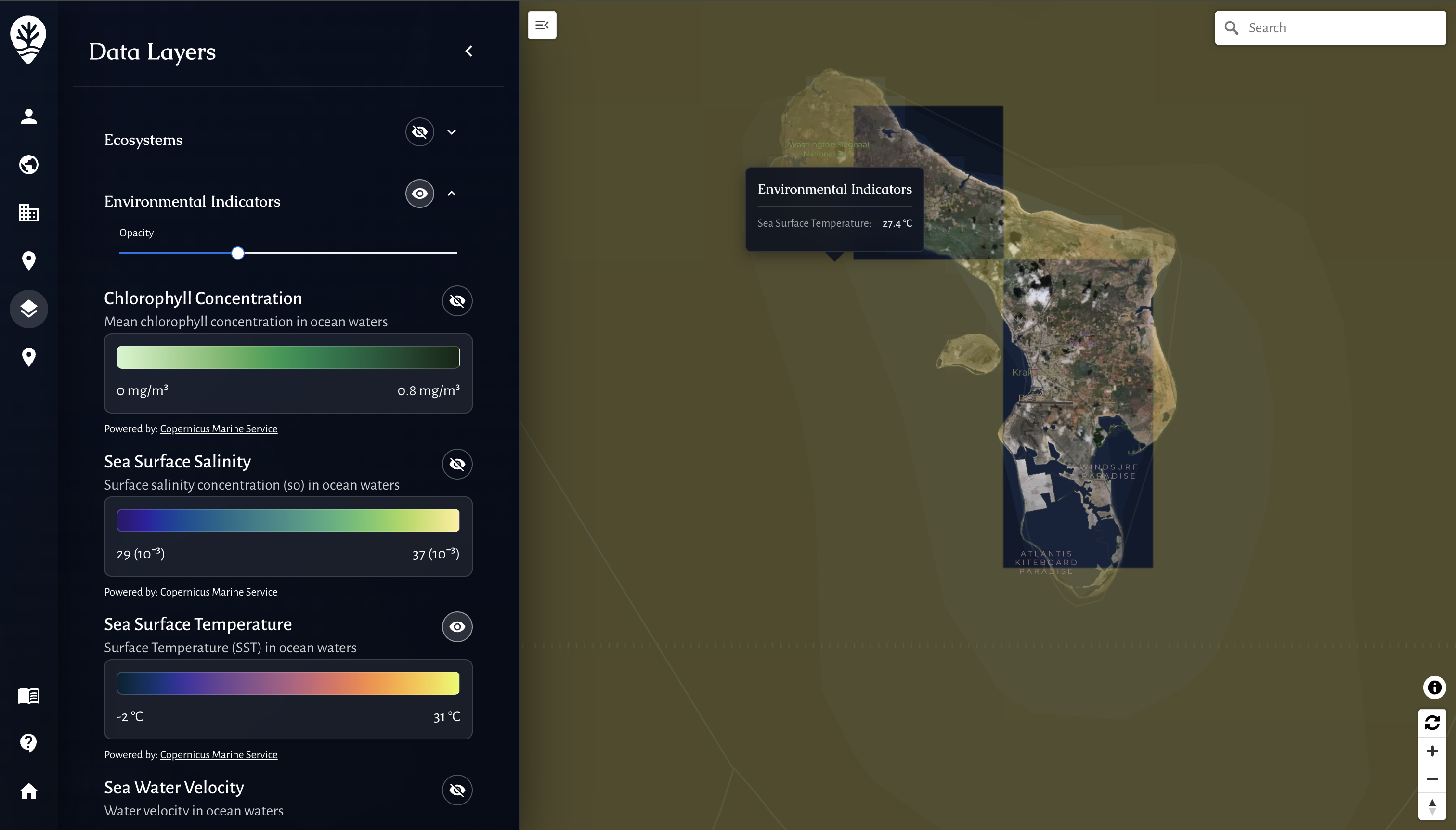
Seagrass Monitoring in MariMap
Seagrass monitoring in MariMap uses repeatable marine survey methods so teams can track seagrass condition over time. Seagrass sites use benthic transects, fish transects, and benthic image surveys, with plan-based geometry that keeps sampling consistent across seasons. This guide explains how to set up seagrass monitoring, capture field observations, and interpret seagrass indicators alongside environmental context.
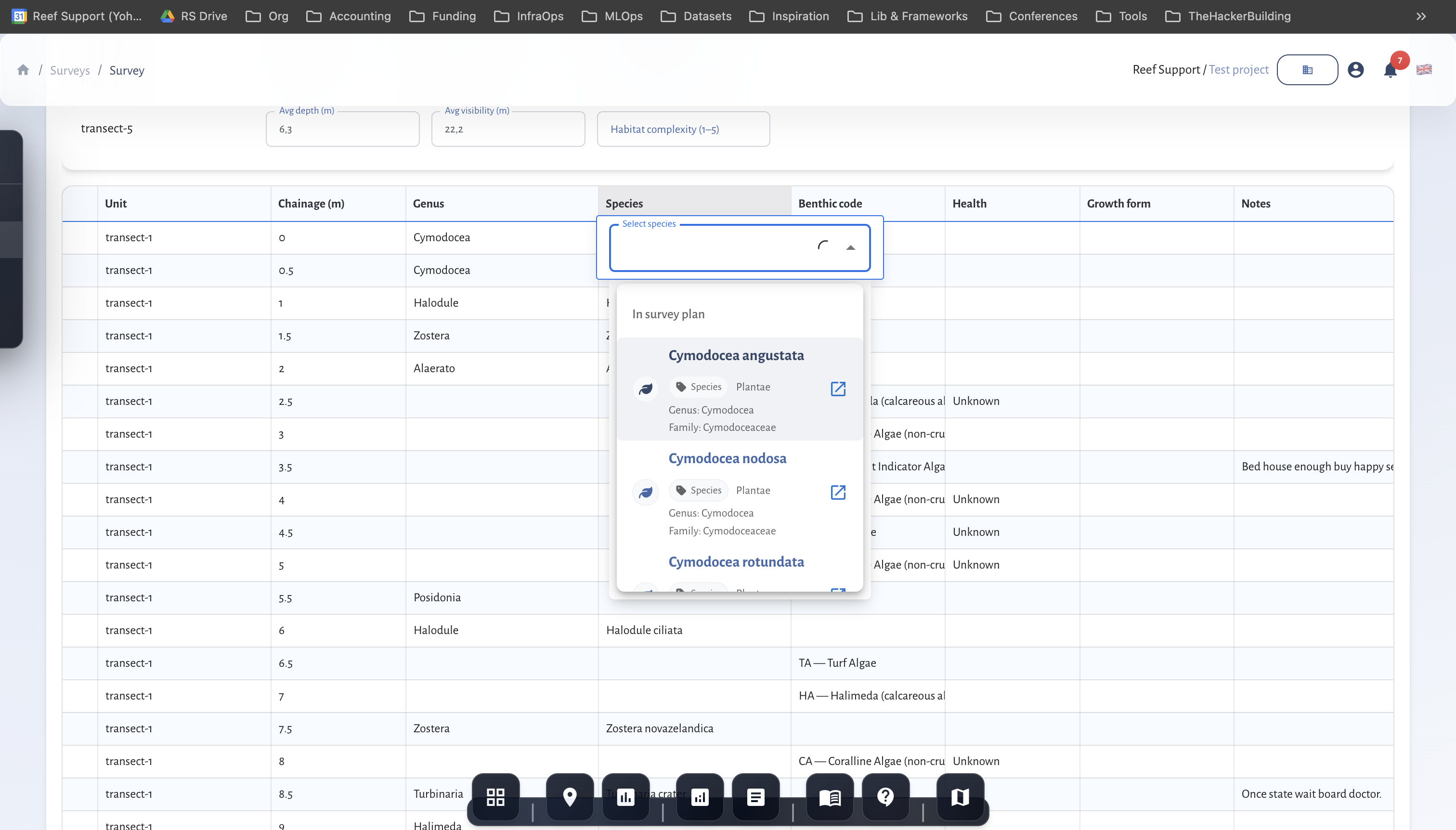
 Benthic transect data entry in MariMap.
Benthic transect data entry in MariMap.
At a glance
- Seagrass monitoring in MariMap uses Benthic transect, Fish transect, and Benthic images protocols.
- Plans keep sampling geometry and photo points consistent across surveys.
- Benthic codes capture seagrass cover, bare substrate, and habitat notes.
- Monitoring metrics appear on the site Monitoring workspace and in Analytics.
- Satellite context supports interpretation of seasonal change.
Before you start
- Confirm the site type is Seagrass in the Site profile.
- Draw or upload a boundary that matches the seagrass footprint.
- Decide which methods you need (cover, imagery, fish community).
- Align on benthic codes or species lists used by your team.
Protocols available in MariMap
Benthic transect (PIT or LIT)
Benthic transects are the core method for documenting seagrass cover and habitat composition. In MariMap you choose PIT or LIT when you create the survey and then record consistent observations along each transect.
Common data captured: benthic codes, seagrass cover notes, substrate type, and field conditions.
Fish transect (belt)
Fish transects capture fish abundance and size classes in seagrass habitats. Use them when fish community indicators are part of your monitoring plan.
Common data captured: species or genus, counts, size class, and notes.
Benthic images
Benthic image surveys organize photo points or quadrats so you can review imagery later. This is helpful for QA/QC and consistent annotation workflows.
Common data captured: image files, photo point ID, depth, and annotation tags.
Choosing the right seagrass monitoring mix
- Seagrass condition baseline: Benthic transect + Benthic images.
- Habitat + fish context: Benthic transect + Fish transect.
- Rapid checks: one protocol with stable geometry and clear notes.
- Restoration monitoring: reuse the same plan and increase repeat frequency.
Step-by-step in MariMap
1) Create a survey plan
- Go to Surveys → Plans.
- Click Create plan and select the seagrass site.
- Choose the protocol (Benthic transect, Fish transect, or Benthic images).
- Draw transects or photo points inside the site boundary.
- Save the plan so the same geometry is reused.
2) Configure method settings
- In Surveys, click Create survey.
- Choose Plan as the source and select your plan.
- Confirm the survey date and team.
- Set method settings:
- Benthic transect: choose PIT or LIT and set interval if needed.
- Fish transect: set belt width and size class defaults.
3) Collect and enter observations
- Use the survey grid to enter seagrass cover and habitat observations.
- Attach photos to benthic image units if you run imagery-based monitoring.
- Add notes for water clarity, current, or unusual conditions.
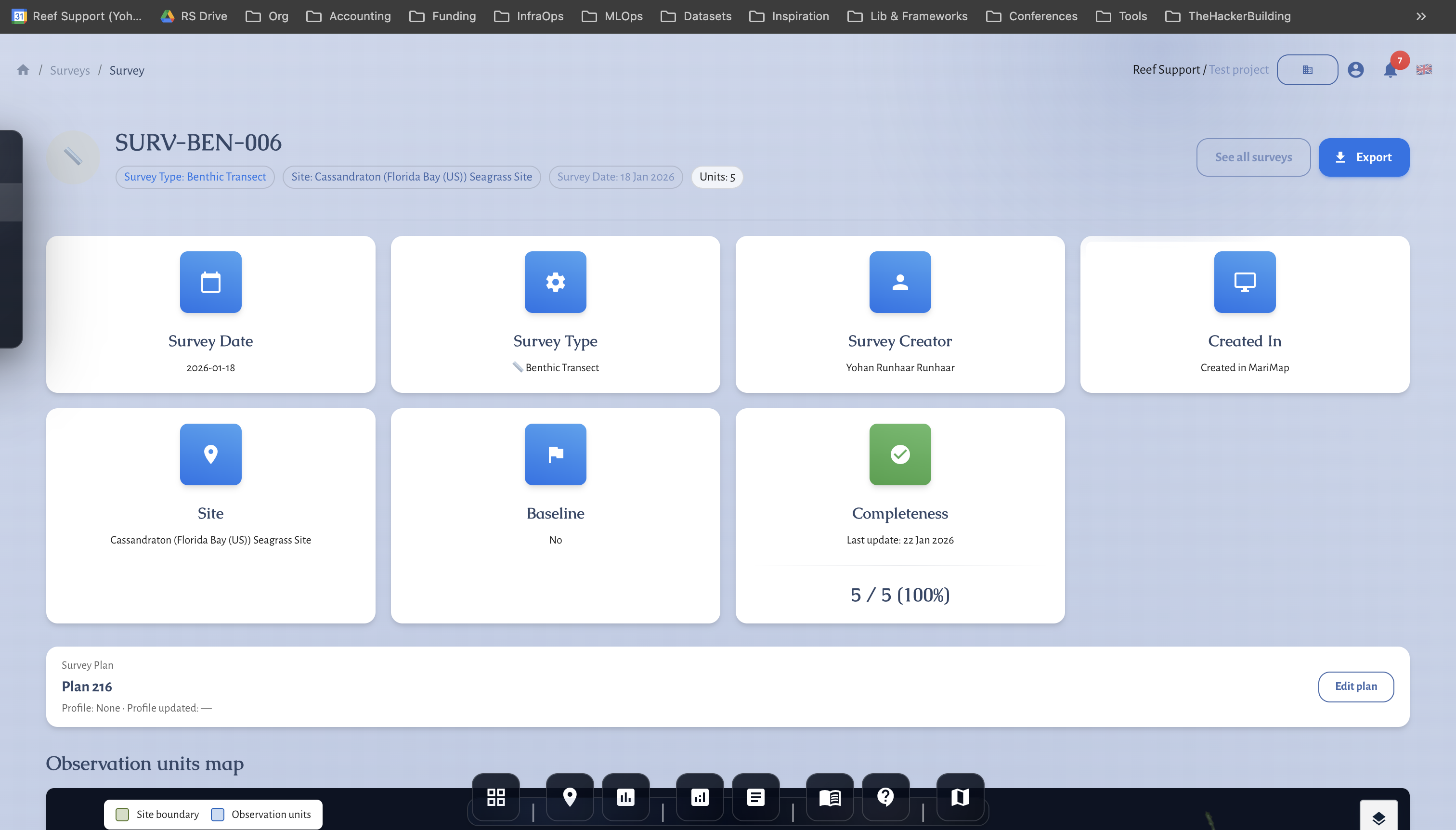
4) Review and complete the survey
- Update the Survey status from In progress → In review → Completed.
- Confirm any outliers or missing fields before closing the survey.
5) Review monitoring metrics
- Open the site page and scroll to Monitoring.
- Check Monitoring overview and Monitoring metrics for trends.
- Use Recent surveys to compare with previous seasons.
Interpreting seagrass monitoring results
Combine benthic cover data, image review, and fish observations to understand seagrass condition. Use Analytics charts and the site environment section to connect changes in seagrass cover with temperature or water quality context. This helps explain seasonal shifts and stress events.
Tips for consistent seagrass monitoring
- Reuse the same plan so transects stay consistent over time.
- Keep benthic codes stable to reduce cleanup work.
- Record key field notes (turbidity, wind, visibility) for QA/QC.
- Review metrics after each survey to catch data gaps early.
Common issues
- No protocols shown: confirm the site type is Seagrass.
- Geometry errors: transects must be inside the site boundary.
- Missing method details: PIT interval or belt width may be required.
MRV readiness and disclosure alignment
- Baseline vs repeat surveys: mark baselines and keep repeat surveys on comparable geometry.
- Monitoring plan logic: define cadence, QA/QC thresholds, and conservative handling of uncertainty.
- Outcome types and claims discipline: record uplift, avoided loss, or maintenance credits; separate inputs from verified outcomes.
- Rights and integrity: document FPIC, customary marine tenure, OECM, ICCA, benefit sharing, durability mechanisms, and leakage risk.
- Disclosure alignment: map indicators to TNFD, CSRD, ESRS, EU Taxonomy, SBTN, and SBTi requirements.
- Use the Metrics Reference and Data Providers for definitions and sources.
Related guides
- Planning Surveys and Data Collection
- Understanding Satellite and Environmental Data
- Generating Reports for Funders and Regulators
References